Background
Cardiac ultrasound is sometimes called echocardiography which is a therapy that involves using sound waves to generate images of the heart. As such, it is a non-invasive and safe procedure which evaluate the anatomy and functioning of the heart.
It is based on the principles of ultrasound technology, it uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs.
Echocardiography involves use of high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) produced by a transducer placed on the skin of the chest. These sound waves then move through the body then if they reach a structure like the heart, some are reflected to the transducer. These returning sound waves are then converted into images by using real time view of the heart’s anatomy and functionality.
Indications
Evaluations of the general configuration and dimensions of the heart, with special emphasis on the number of chambers, valves, and prominent blood vessels.
Evaluation of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) to obtain information in concern with the ability of heart to pump.
Assessment of wall motion abnormalities indicates to ischemic heart disease or other heart diseases.
Assessment of the heart valve function of include the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, and pulmonic valves.
Evaluation of different types of Congestive Heart failure specially, diagnosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy, Restrictive Cardiomyopathy.
Detection of regional wall motion abnormality that may lead to myocardial ischemia of the LV.
Coronary evaluation such as echocardiographic examinations. Echocardiography plays a significant role in cardiology to diagnose and to evaluate different diseases of the heart muscles, valves, birth defects in heart, congestive heart failure or coronary artery diseases.
Contraindications
Ultrasound should not be carried out over open wounds, cuts, or parts that have active infections to present the risk of introducing bacteria into the bloodstream or causes pain.
Patients who cannot sit still or cannot cooperate may find it almost impossible to have clear images obtained during the procedure. This is even more so seen in pediatric patients or patients with other cognitive abnormalities.
There are also some contraindications, especially when one has just had recent trauma or surgery of the chest area, especially involving an area that the ultrasound transducer will be applied over, for possible discomfort or damage to healing tissues.
Certain skin conditions in an area to which an ultrasound transducer is applied can make achieving clear images difficult. Open sores, severe rashes or skin lesions may be considered.
In transesophageal echocardiography, when a probe is placed into the esophagus to visualize images, patients with esophageal strictures, varices, or other lesions are considered careful candidates.
Outcomes
Echocardiology gives the size and the measurement of parts of the heart such as; left ventricle, right ventricle, atria and septum. Tests the mitral, aortic, tricuspid and pulmonic valves of the heart for diseases such a stenosis or regurgitation.
Estimation of the fraction of blood sent out by the left ventricle in each beat that gives information about the pumped function of the heart.
Recognition of any structure’s movement or dysfunction of the heart walls that can present ischemia or various cardiac diseases.
Presence of any irregularity or disfunction of the walls of the heart, which may point to ischemia or other heart diseases.
Evaluation of flow of blood through the heart’s valves with an aim of identifying regurgitation or stenosis.
Doppler ultrasounds help to estimate blood flow velocity in any areas of heart chamber and blood vessels.
Recognition of congenital anomalies in the structure present at birth. Identification of factors influencing the capacity for work in patients with disorders of the heart muscle, including hypertrophic, dilated, and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
Periprocedural care
Equipment
Ultrasound Machine
Ultrasound Transducer
Electrocardiogram System
Gel
Patient Monitoring Equipment
Patient Preparation
Informed Consent:
Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
Patient Positioning:
For a standard echocardiogram, position the patient comfortably on an examination table resting on their left side while in the process of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), the patient should sit with semi upright position.
Technique
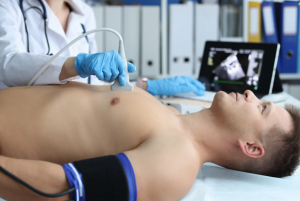
Cardiac ultrasound
There are two primary types of cardiac ultrasound: transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE).
Step 1: Application of Gel:
Preparing the surface of the patient’s chest, a water base gel is used. As a result, the transmission of ultrasound waves is enhanced, and clear visualization is achieved.
Step 2: Placement of Transducer:
Ultrasound transducer emits and receives ultrasound waves that are positioned in different locations on chest to capture different chambers of the heart. Parasternal, apical and intercostal oblique, and subcostal views are employed to capture optimal images of the heart.
Step 3: Image capturing
Take enough images to evaluate chambers, valves, and determine the function of the heart.
Step 4: Probe Manipulation
In some cases, the patient must switch positions or, breathe in a certain way to get optimal image quality and to evaluate different aspects of cardiac performance.
Various views allow for a detailed examination of different aspects of the heart as follows:
Parasternal long-axis view: It is a side view of the heart, showing the left ventricle, aorta, and mitral valve.
Apical Four-Chamber View: This takes pictures of all four chambers of the heart (left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, and right ventricle).
Apical Two-Chamber View: The left atrium and ventricle of the view that is shown provide a longitudinal view of the left side of heart.
It supports the four-chamber view in its entirety to give a more complete assessment.
Mid-esophageal four-chamber view: It is essentially the transthoracic apical four-chamber view but obtained through the esophagus.
Trans gastric Short-Axis View: Obtained by angling the TEE probe into the stomach by providing a short-axis view of the left ventricle.
4.Complications
Complication arising from sedation includes respiratory suppression, allergy on the sedation agents used and effects arising from sedation on specific respiratory disease.
Insertion of the TEE probe may cause minor damage to the esophageal lining.
Formation of a perforation, a very rare but serious complication, may also occur.
The gag reflex is elicited in TEE, and if previous measures are not applied, aspiration can occur.
There are possibilities of these changes being more sensitive to cardiovascular illnesses patients. The TEE probe is placed in the mouth, it rarely causes dental damage, but if a bite block is not used, or there is pathologic change in the teeth.

Cardiac ultrasound is sometimes called echocardiography which is a therapy that involves using sound waves to generate images of the heart. As such, it is a non-invasive and safe procedure which evaluate the anatomy and functioning of the heart.
It is based on the principles of ultrasound technology, it uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs.
Echocardiography involves use of high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) produced by a transducer placed on the skin of the chest. These sound waves then move through the body then if they reach a structure like the heart, some are reflected to the transducer. These returning sound waves are then converted into images by using real time view of the heart’s anatomy and functionality.
Evaluations of the general configuration and dimensions of the heart, with special emphasis on the number of chambers, valves, and prominent blood vessels.
Evaluation of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) to obtain information in concern with the ability of heart to pump.
Assessment of wall motion abnormalities indicates to ischemic heart disease or other heart diseases.
Assessment of the heart valve function of include the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, and pulmonic valves.
Evaluation of different types of Congestive Heart failure specially, diagnosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy, Restrictive Cardiomyopathy.
Detection of regional wall motion abnormality that may lead to myocardial ischemia of the LV.
Coronary evaluation such as echocardiographic examinations. Echocardiography plays a significant role in cardiology to diagnose and to evaluate different diseases of the heart muscles, valves, birth defects in heart, congestive heart failure or coronary artery diseases.
Ultrasound should not be carried out over open wounds, cuts, or parts that have active infections to present the risk of introducing bacteria into the bloodstream or causes pain.
Patients who cannot sit still or cannot cooperate may find it almost impossible to have clear images obtained during the procedure. This is even more so seen in pediatric patients or patients with other cognitive abnormalities.
There are also some contraindications, especially when one has just had recent trauma or surgery of the chest area, especially involving an area that the ultrasound transducer will be applied over, for possible discomfort or damage to healing tissues.
Certain skin conditions in an area to which an ultrasound transducer is applied can make achieving clear images difficult. Open sores, severe rashes or skin lesions may be considered.
In transesophageal echocardiography, when a probe is placed into the esophagus to visualize images, patients with esophageal strictures, varices, or other lesions are considered careful candidates.
Echocardiology gives the size and the measurement of parts of the heart such as; left ventricle, right ventricle, atria and septum. Tests the mitral, aortic, tricuspid and pulmonic valves of the heart for diseases such a stenosis or regurgitation.
Estimation of the fraction of blood sent out by the left ventricle in each beat that gives information about the pumped function of the heart.
Recognition of any structure’s movement or dysfunction of the heart walls that can present ischemia or various cardiac diseases.
Presence of any irregularity or disfunction of the walls of the heart, which may point to ischemia or other heart diseases.
Evaluation of flow of blood through the heart’s valves with an aim of identifying regurgitation or stenosis.
Doppler ultrasounds help to estimate blood flow velocity in any areas of heart chamber and blood vessels.
Recognition of congenital anomalies in the structure present at birth. Identification of factors influencing the capacity for work in patients with disorders of the heart muscle, including hypertrophic, dilated, and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
Equipment
Ultrasound Machine
Ultrasound Transducer
Electrocardiogram System
Gel
Patient Monitoring Equipment
Patient Preparation
Informed Consent:
Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
Patient Positioning:
For a standard echocardiogram, position the patient comfortably on an examination table resting on their left side while in the process of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), the patient should sit with semi upright position.

Cardiac ultrasound
There are two primary types of cardiac ultrasound: transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE).
Step 1: Application of Gel:
Preparing the surface of the patient’s chest, a water base gel is used. As a result, the transmission of ultrasound waves is enhanced, and clear visualization is achieved.
Step 2: Placement of Transducer:
Ultrasound transducer emits and receives ultrasound waves that are positioned in different locations on chest to capture different chambers of the heart. Parasternal, apical and intercostal oblique, and subcostal views are employed to capture optimal images of the heart.
Step 3: Image capturing
Take enough images to evaluate chambers, valves, and determine the function of the heart.
Step 4: Probe Manipulation
In some cases, the patient must switch positions or, breathe in a certain way to get optimal image quality and to evaluate different aspects of cardiac performance.
Various views allow for a detailed examination of different aspects of the heart as follows:
Parasternal long-axis view: It is a side view of the heart, showing the left ventricle, aorta, and mitral valve.
Apical Four-Chamber View: This takes pictures of all four chambers of the heart (left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, and right ventricle).
Apical Two-Chamber View: The left atrium and ventricle of the view that is shown provide a longitudinal view of the left side of heart.
It supports the four-chamber view in its entirety to give a more complete assessment.
Mid-esophageal four-chamber view: It is essentially the transthoracic apical four-chamber view but obtained through the esophagus.
Trans gastric Short-Axis View: Obtained by angling the TEE probe into the stomach by providing a short-axis view of the left ventricle.
4.Complications
Complication arising from sedation includes respiratory suppression, allergy on the sedation agents used and effects arising from sedation on specific respiratory disease.
Insertion of the TEE probe may cause minor damage to the esophageal lining.
Formation of a perforation, a very rare but serious complication, may also occur.
The gag reflex is elicited in TEE, and if previous measures are not applied, aspiration can occur.
There are possibilities of these changes being more sensitive to cardiovascular illnesses patients. The TEE probe is placed in the mouth, it rarely causes dental damage, but if a bite block is not used, or there is pathologic change in the teeth.

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



