Background
Dermabrasion is a treatment that is intended to refine the look and texture of the skin. It is the process of using machines; the skin surface is exfoliated to get rid of the dead skin cells. This, in turn, promotes the growth of newer skin cells, thus promoting the development of a much smoother skin tone.
Dermabrasion involves the epidermis and the shallow dermal layer of skin, where all the deformities such as skin scars, wrinkles, and uneven colorations exist. This is because dermabrasion eliminates these damaged layers with the implication of regrowing healthier skin cells.
When doing dermabrasion, there is a need to use an instrument like rotary instrument or wire brush to rub the skin’s surface. This controlled abrasing exfoliates or rubs off the outer surface layers of the skin comprising of, the dead skin layers, scar tissues and other skin irregularities. It also activates collagen formation and increases the rate of skin cells turnover hence promoting the formation of young-looking skin.
Indications
Acne Scars: Dermabrasion is also beneficial in the treatment of acne scars as it involves the removal of the upper layer of skin to promote the formation of new skin.
Wrinkles and Fine Lines: It reduces the fine lines and wrinkle by allowing collagen remodelling and skin tightening as a method of making the skin youthful again.
Hyperpigmentation: As the dermabrasion aims at the removal of some layers of the pigmented skin, it can brighten as well as correct the skin tone thus enhancing the skin’s complexion.
Sun Damage: Also known as derma resting, dermabrasion helps enhance the skin tone especially in areas that have been affected by excessive sun exposure such as uneven skin tone, freckles.
Scar Revision: This treatment can be applied to injuries that may have caused scars on the skin or after surgeries and traumatic events as it helps to level the scar and make it present a smooth skin texture with the rest of the skin.
Actinic Keratoses: Actinic keratoses that are precancerous can be eliminated by dermabrasion, which lowers the possibility of forming skin cancer and enhances the appearance of the skin.
Seborrheic Keratoses: Facial dermabrasion can easily treat one common skin condition, seborrheic keratosis which are growths that are benign on the skin and improve the general skin texture with the added benefit that the patient will have minimal, mild or no irritation or discomfort.
Contraindications
Active Infections: Dermabrasion should not be done where the skin is infected or inflamed. These include the viral diseases for example herpes simplex virus (cold sores), bacterial diseases and the fungal one. Infections are bound to occur when dermabrasion is carried out on infected skins since it will only help in spreading the infection as well as lead to other complications.
Active Acne: Dermabrasion is not advisable in patients with sharp acne breakouts. This procedure can even aggravate acne and thereby cause scarring. It is recommended not to go through dermabrasion immediately when having acne.
Skin Conditions: People having skin diseases may not be good candidate for dermabrasion since the scarring, pigmentation and skin condition such as eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis and rosacea can be worsened.
Recent Chemical Peel or Laser Resurfacing: People who have had a recent chemical peel or laser resurfacing must wait until the skin in the treatment area has healed itself properly.
Outcomes
Scar Reduction: Dermabrasion is useful in removal of acne scars, surgical marks and marks resulting from injuries. It may be useful in fading of the edges of a scar and make them almost invisible from the skin surrounding them.
Wrinkle Reduction: In this case, dermabrasion may be used to reduce the fine lines and wrinkles as it assists in collagen remodelling hence tightens the skin and thus giving the skin a youthful appearance.
Hyperpigmentation Improvement: Dermabrasion reduces the melanocyte production in terms of their capacity in making pigments to lighter skin tone since the instrument removes the pigmented skin cells which identify degree of hyperpigmentation.
Sun Damage Repair: Dermabrasion aims at enhancing the external look of the skin especially that with sun induced.
Improved Skin Texture: Skin tone can be refined by dermabrasion as it eliminates skin roughness and wrinkles, thus making the skin tone to be even.
Enhanced Skin Absorption: Dermabrasion also helps in improving the results of the skincare product by eliminating the outer layer of the skin to make the product to penetrate easily.
Equipment
Dermabrasion Device
Suction Device
Anesthesia Equipment
Protective Gear
Sterilization Equipment:
Topical Agents
Dermabrasion Device
Patient preparation
Skin Preconditioning: Preconditioning of the skin can also enhance the outcome of dermabrasion and reduce chance of complications. This may include application of topical retinoids or alpha hydroxy acids to make the skin layer thinner, to enable effective penetration of the dermabrasion device.
Skin Care Regimen: A patient might be advised to adopt a specific skin care regime before the process of dermabrasion is conducted. This may range from washing the skin with soap and water and avoiding scrubs and any other products that may be abrasive to the skin.
Sun Protection: The patient is thus asked to avoid direct exposure to the sun and ensure that they apply sunscreen to minimize the impacts of the sun on skin which are known to influence the results of dermabrasion.
Medical History Review: It is crucial that the healthcare provider should go through the patient’s medical history and check whether there are any complications that may arise from this procedure.
Informed Consent: Patients should be given some information about dermabrasion benefits and the risks involved in the process so that they should give their informed consent before the process is performed on them. They should also have the right expectation on the outcomes of dermabrasion.
Technique
Dermabrasion is a technique applied to enhance skin by exfoliating all the skin surfaces. It includes the exfoliation of skin layers especially the epidermis and some part of dermis through a device provided with an abrasive surface. This procedure helps in collagen synthesis and skin regeneration.
Step 1: Patient Evaluation and Preparation
A patient going through dermabrasion must undergo some examination to choose whether they are eligible for the process, depending on factors such as skin type, medical history, or aesthetic expectations. After the assessment of the patient’s candidacy for dermabrasion, the proper medical pre-emptive measures and skin preparation procedure can be initiated to improve the efficacy of the procedure as well as reduce the likelihood of adverse effects.
Step 2: Anesthesia Administration
Dermabrasion can be carried out usually under local anesthesia depending to the procedure done and the patient feeling. In most cases, local anesthesia is employed and may include the use of lidocaine or similar agents to reduce the pain that the patient may undergo during the procedure.
Step 3: Preparing the Skin
In preparing for dermabrasion, the area of the skin that will undergo the treatment should be cleaned and devoid of make-up, oils, or any substances that may hinder the entire procedure. This is done gently using a mild cleanser to clean the skin so that it does not hold any contaminants. After the skin has been washed, it is common to draw the treatment area with a skin marking pen, which may be a surgical marker. This helps in administering correct dosage and prevents variation within the individual-group and provides the healthcare provider with an opportunity to avoid sophisticated regions of the body such as the eye and lips.
Step 4: Choice of a Derma abrasion Device
The choice of the dermabrasion device depends on characteristics such as skin type of the patient, the skin condition that needs to be treated and the required treatment depth. The common dermabrasion instruments include the diamond-tip wands, wire brushes and rotary instruments having abrasive surfaces. The type of the device must be chosen depending on the patient’s skin type and the area that will be treated.
Step 5: Dermabrasion Technique
Once, the treatment area is cleared and ready together with the suitable anesthesia, then dermabrasion can be done. A rotary appliance is used by the healthcare provider to abrade the skin with specified force and direction to exfoliate the outer layers of the skin. The treatment can be made deeper depending on the type of skin as well as outcomes that are planned on achieving. Patients with dermatological disorders must have their skin’s reaction to the dermabrasion process carefully observed by the healthcare provider as they modify the process if necessary to get the most desirable results with minimal adverse effects.
Step 6: Postoperative Care
After the dermabrasion procedure is over then, the treatment area is cleaned and then covered with protective ointment or dressing to avoid infection. Some may develop mild inflammation and slight soreness in the days that follow the procedure, and these are usually relieved by over-the-counter analgesics and the application of ice packs
Step 7: Follow-up and Monitoring
A couple of weeks or months later, the patient must undergo follow-up sessions for check-ups and to evaluate the effectiveness of the dermabrasion. In the follow-up visits, the provider examines the progress of the wound healing, and other related issues, examine for any complication which may have arisen and advises on or administers other measures pertinent to aid the healing process or enhance the results.
Standard technique
Dermabrasion of scars
Throughout the procedure the reaction of the skin is observed, and the method is modified accordingly to accomplish the best results. There should not be any sort of over-treatment or putting pressure on the patients as it may lead to development of scar or infection. When the dermabrasion is done, the dermatologist washes the area and applies a topical agent such as an antibiotic ointment or dressing. After procedure, patients are provided with guidelines for wound care as well as instructions on how to protect their skin from the harmful UV-rays along with appointments aimed at the control of the healing process and evaluation of the outcomes.

Dermabrasion of scars
Advanced technique
Advanced dermabrasion techniques have been developed to improve the safety and efficacy, allowing for more precise and controlled skin exfoliation. These techniques are often used for complex cases or to achieve more dramatic results.
One advanced technique is “feather edging,” which involves blending the edges of the treated area with the surrounding skin to create a smoother transition and reduce the risk of noticeable demarcation lines. This technique requires a skilled practitioner who can control the depth and pressure of the dermabrasion device to achieve a seamless result.
Another advanced technique is “subcision,” when the subcutaneous fatty tissue is mechanically separated from the dermis, and then the two layers are reunited at a higher level, which is often applied in conjunction with dermabrasion to treat deeper wrinkles. Several techniques are used depending on the severity of the scar; subcision is where the dermatologist uses a needle or blade to cut through fibrous bands that are pulling the skin down and causing the indentations. This makes it possible to spread pressure evenly on the skin and this improves the conditions of the skin such as the scars and wrinkles.
In some cases, sophisticated dermabrasion may be accomplished by employing equipment such as the fractionated lasers or microneedling devises to thoroughly and selectively remove layers of the skin.
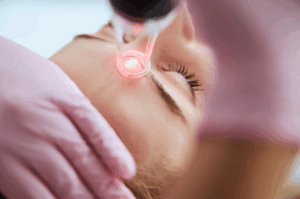
Fractionated lasers or micro needling
Complications
Pigment Changes: After dermabrasion there may be slight variations in skin colour or tone and this results into hypopigmentation and hyper pigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation: The side effects of the dermabrasion for instance results in an over production of pigment of the skin hence leading to dark areas.
Hypopigmentation: Dermabrasion also affects the skin in that it can make skin produce less pigment, which causes lightening. This is more prevalent in people with fair skin as compared to dark-skinned persons.
Persistent Redness: There may be skin’s redness that lasts for many days after dermabrasion known as erythema in some people. This is primarily a period which could be short but, in some instances, it may be protracted.
Acne Flare-ups: In some instances, there are side effects of dermabrasion that cause acne formation, and these are common in people with a history of acne formation. This risk can be minimized when adequate measures have been undertaken in the postoperative care especially concerning the patient’s skin.
Allergic Reactions: There are side effects that may be caused by anesthesia or drugs administered throughout the process to the patients. This could present itself as itching, rash, or swelling.
Medication Summary
Local Anesthetics
Antibiotics
Antiviral Medications
Topical Retinoids
Steroids
Sunscreen
Moisturizers
References
Medication
References

Dermabrasion is a treatment that is intended to refine the look and texture of the skin. It is the process of using machines; the skin surface is exfoliated to get rid of the dead skin cells. This, in turn, promotes the growth of newer skin cells, thus promoting the development of a much smoother skin tone.
Dermabrasion involves the epidermis and the shallow dermal layer of skin, where all the deformities such as skin scars, wrinkles, and uneven colorations exist. This is because dermabrasion eliminates these damaged layers with the implication of regrowing healthier skin cells.
When doing dermabrasion, there is a need to use an instrument like rotary instrument or wire brush to rub the skin’s surface. This controlled abrasing exfoliates or rubs off the outer surface layers of the skin comprising of, the dead skin layers, scar tissues and other skin irregularities. It also activates collagen formation and increases the rate of skin cells turnover hence promoting the formation of young-looking skin.
Acne Scars: Dermabrasion is also beneficial in the treatment of acne scars as it involves the removal of the upper layer of skin to promote the formation of new skin.
Wrinkles and Fine Lines: It reduces the fine lines and wrinkle by allowing collagen remodelling and skin tightening as a method of making the skin youthful again.
Hyperpigmentation: As the dermabrasion aims at the removal of some layers of the pigmented skin, it can brighten as well as correct the skin tone thus enhancing the skin’s complexion.
Sun Damage: Also known as derma resting, dermabrasion helps enhance the skin tone especially in areas that have been affected by excessive sun exposure such as uneven skin tone, freckles.
Scar Revision: This treatment can be applied to injuries that may have caused scars on the skin or after surgeries and traumatic events as it helps to level the scar and make it present a smooth skin texture with the rest of the skin.
Actinic Keratoses: Actinic keratoses that are precancerous can be eliminated by dermabrasion, which lowers the possibility of forming skin cancer and enhances the appearance of the skin.
Seborrheic Keratoses: Facial dermabrasion can easily treat one common skin condition, seborrheic keratosis which are growths that are benign on the skin and improve the general skin texture with the added benefit that the patient will have minimal, mild or no irritation or discomfort.
Active Infections: Dermabrasion should not be done where the skin is infected or inflamed. These include the viral diseases for example herpes simplex virus (cold sores), bacterial diseases and the fungal one. Infections are bound to occur when dermabrasion is carried out on infected skins since it will only help in spreading the infection as well as lead to other complications.
Active Acne: Dermabrasion is not advisable in patients with sharp acne breakouts. This procedure can even aggravate acne and thereby cause scarring. It is recommended not to go through dermabrasion immediately when having acne.
Skin Conditions: People having skin diseases may not be good candidate for dermabrasion since the scarring, pigmentation and skin condition such as eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis and rosacea can be worsened.
Recent Chemical Peel or Laser Resurfacing: People who have had a recent chemical peel or laser resurfacing must wait until the skin in the treatment area has healed itself properly.
Scar Reduction: Dermabrasion is useful in removal of acne scars, surgical marks and marks resulting from injuries. It may be useful in fading of the edges of a scar and make them almost invisible from the skin surrounding them.
Wrinkle Reduction: In this case, dermabrasion may be used to reduce the fine lines and wrinkles as it assists in collagen remodelling hence tightens the skin and thus giving the skin a youthful appearance.
Hyperpigmentation Improvement: Dermabrasion reduces the melanocyte production in terms of their capacity in making pigments to lighter skin tone since the instrument removes the pigmented skin cells which identify degree of hyperpigmentation.
Sun Damage Repair: Dermabrasion aims at enhancing the external look of the skin especially that with sun induced.
Improved Skin Texture: Skin tone can be refined by dermabrasion as it eliminates skin roughness and wrinkles, thus making the skin tone to be even.
Enhanced Skin Absorption: Dermabrasion also helps in improving the results of the skincare product by eliminating the outer layer of the skin to make the product to penetrate easily.
Dermabrasion Device
Suction Device
Anesthesia Equipment
Protective Gear
Sterilization Equipment:
Topical Agents
Dermabrasion Device
Patient preparation
Skin Preconditioning: Preconditioning of the skin can also enhance the outcome of dermabrasion and reduce chance of complications. This may include application of topical retinoids or alpha hydroxy acids to make the skin layer thinner, to enable effective penetration of the dermabrasion device.
Skin Care Regimen: A patient might be advised to adopt a specific skin care regime before the process of dermabrasion is conducted. This may range from washing the skin with soap and water and avoiding scrubs and any other products that may be abrasive to the skin.
Sun Protection: The patient is thus asked to avoid direct exposure to the sun and ensure that they apply sunscreen to minimize the impacts of the sun on skin which are known to influence the results of dermabrasion.
Medical History Review: It is crucial that the healthcare provider should go through the patient’s medical history and check whether there are any complications that may arise from this procedure.
Informed Consent: Patients should be given some information about dermabrasion benefits and the risks involved in the process so that they should give their informed consent before the process is performed on them. They should also have the right expectation on the outcomes of dermabrasion.
Dermabrasion is a technique applied to enhance skin by exfoliating all the skin surfaces. It includes the exfoliation of skin layers especially the epidermis and some part of dermis through a device provided with an abrasive surface. This procedure helps in collagen synthesis and skin regeneration.
Step 1: Patient Evaluation and Preparation
A patient going through dermabrasion must undergo some examination to choose whether they are eligible for the process, depending on factors such as skin type, medical history, or aesthetic expectations. After the assessment of the patient’s candidacy for dermabrasion, the proper medical pre-emptive measures and skin preparation procedure can be initiated to improve the efficacy of the procedure as well as reduce the likelihood of adverse effects.
Step 2: Anesthesia Administration
Dermabrasion can be carried out usually under local anesthesia depending to the procedure done and the patient feeling. In most cases, local anesthesia is employed and may include the use of lidocaine or similar agents to reduce the pain that the patient may undergo during the procedure.
Step 3: Preparing the Skin
In preparing for dermabrasion, the area of the skin that will undergo the treatment should be cleaned and devoid of make-up, oils, or any substances that may hinder the entire procedure. This is done gently using a mild cleanser to clean the skin so that it does not hold any contaminants. After the skin has been washed, it is common to draw the treatment area with a skin marking pen, which may be a surgical marker. This helps in administering correct dosage and prevents variation within the individual-group and provides the healthcare provider with an opportunity to avoid sophisticated regions of the body such as the eye and lips.
Step 4: Choice of a Derma abrasion Device
The choice of the dermabrasion device depends on characteristics such as skin type of the patient, the skin condition that needs to be treated and the required treatment depth. The common dermabrasion instruments include the diamond-tip wands, wire brushes and rotary instruments having abrasive surfaces. The type of the device must be chosen depending on the patient’s skin type and the area that will be treated.
Step 5: Dermabrasion Technique
Once, the treatment area is cleared and ready together with the suitable anesthesia, then dermabrasion can be done. A rotary appliance is used by the healthcare provider to abrade the skin with specified force and direction to exfoliate the outer layers of the skin. The treatment can be made deeper depending on the type of skin as well as outcomes that are planned on achieving. Patients with dermatological disorders must have their skin’s reaction to the dermabrasion process carefully observed by the healthcare provider as they modify the process if necessary to get the most desirable results with minimal adverse effects.
Step 6: Postoperative Care
After the dermabrasion procedure is over then, the treatment area is cleaned and then covered with protective ointment or dressing to avoid infection. Some may develop mild inflammation and slight soreness in the days that follow the procedure, and these are usually relieved by over-the-counter analgesics and the application of ice packs
Step 7: Follow-up and Monitoring
A couple of weeks or months later, the patient must undergo follow-up sessions for check-ups and to evaluate the effectiveness of the dermabrasion. In the follow-up visits, the provider examines the progress of the wound healing, and other related issues, examine for any complication which may have arisen and advises on or administers other measures pertinent to aid the healing process or enhance the results.
Dermabrasion of scars
Throughout the procedure the reaction of the skin is observed, and the method is modified accordingly to accomplish the best results. There should not be any sort of over-treatment or putting pressure on the patients as it may lead to development of scar or infection. When the dermabrasion is done, the dermatologist washes the area and applies a topical agent such as an antibiotic ointment or dressing. After procedure, patients are provided with guidelines for wound care as well as instructions on how to protect their skin from the harmful UV-rays along with appointments aimed at the control of the healing process and evaluation of the outcomes.

Dermabrasion of scars
Advanced technique
Advanced dermabrasion techniques have been developed to improve the safety and efficacy, allowing for more precise and controlled skin exfoliation. These techniques are often used for complex cases or to achieve more dramatic results.
One advanced technique is “feather edging,” which involves blending the edges of the treated area with the surrounding skin to create a smoother transition and reduce the risk of noticeable demarcation lines. This technique requires a skilled practitioner who can control the depth and pressure of the dermabrasion device to achieve a seamless result.
Another advanced technique is “subcision,” when the subcutaneous fatty tissue is mechanically separated from the dermis, and then the two layers are reunited at a higher level, which is often applied in conjunction with dermabrasion to treat deeper wrinkles. Several techniques are used depending on the severity of the scar; subcision is where the dermatologist uses a needle or blade to cut through fibrous bands that are pulling the skin down and causing the indentations. This makes it possible to spread pressure evenly on the skin and this improves the conditions of the skin such as the scars and wrinkles.
In some cases, sophisticated dermabrasion may be accomplished by employing equipment such as the fractionated lasers or microneedling devises to thoroughly and selectively remove layers of the skin.

Fractionated lasers or micro needling
Pigment Changes: After dermabrasion there may be slight variations in skin colour or tone and this results into hypopigmentation and hyper pigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation: The side effects of the dermabrasion for instance results in an over production of pigment of the skin hence leading to dark areas.
Hypopigmentation: Dermabrasion also affects the skin in that it can make skin produce less pigment, which causes lightening. This is more prevalent in people with fair skin as compared to dark-skinned persons.
Persistent Redness: There may be skin’s redness that lasts for many days after dermabrasion known as erythema in some people. This is primarily a period which could be short but, in some instances, it may be protracted.
Acne Flare-ups: In some instances, there are side effects of dermabrasion that cause acne formation, and these are common in people with a history of acne formation. This risk can be minimized when adequate measures have been undertaken in the postoperative care especially concerning the patient’s skin.
Allergic Reactions: There are side effects that may be caused by anesthesia or drugs administered throughout the process to the patients. This could present itself as itching, rash, or swelling.
Local Anesthetics
Antibiotics
Antiviral Medications
Topical Retinoids
Steroids
Sunscreen
Moisturizers

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



