Background
Esophagography is a radiographic (X-ray) examination study of the esophagus. It includes ingesting barium or water-soluble contrast to visualize esophageal structure and function.
Barium sulfate was introduced in the 1900s to enhance gastrointestinal tract imaging
Fluoroscopy enhanced esophagography for real-time swallowing assessment.
Non-invasive procedure using barium sulfate to outline the esophagus.
Barium esophagography assesses swallowing, motility, reflux, and structural abnormalities of the esophagus and pharynx.
The pharyngeal phase involves dynamic recordings and double-contrast images to assess oral and pharyngeal function.
The risk of aspiration pneumonia increased with swallowing dysfunction while patients with silent aspiration faced nearly 15 times greater risk than those with normal swallowing.
Patient gulps low-density barium to distend esophagus and identify potential rings or strictures
Indications
Indications:
Structural abnormalities
Motility disorders
Foreign body obstruction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Post-surgical evaluation
Dysphagia
Odynophagia
Esophageal Obstruction
Contraindications
Contraindications:
Known or Suspected Barium Allergy
Acute Esophageal Perforation
Severe Dysphagia or Aspiration Risk
Suspected Tracheoesophageal
Severe Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Severe Debilitation
Outcomes
Outcomes:
The test offers essential diagnostic insights for esophageal management and function.
Cervical webs show as thin folds in anterior cervical esophagus barium studies.
Webs may extend circumferentially with deeper anterior shelf. Many patients show no symptoms, but dysphagia occurs with over 50% lumen obstruction.
Ruptured cervical esophageal webs are unrecognizable during endoscopy.
Frontal and lateral double-contrast views in pharyngeal cancer patients show contour disruption due to a mass protruding into the lumen.
Equipment required
Fluoroscopy Unit
X-ray Generator & Digital Recorder
Lead Shields & Radiation Protection Gear
Ancillary Equipment & Supplies
Patient Preparation
Patients must fast 4 to 8 hours before the procedure for clear esophagus views.
Patients on diabetes medications may need dose adjustments while fasting.
Check for barium or iodine allergy before using contrast agents.
Minimize radiation exposure for pregnant patients. Evaluate aspiration risk for stroke and neuromuscular patients.
Informed Consent:
Explain the procedure’s risks and potential complications clearly to the patient.
Patient Positioning
Patient should be positioned in upright and supine position for a complete assessment.
Patient examined upright and supine to assess entire esophagus.
Technique
Step 1: Administration of Contrast
Barium sulfate is preferred for most cases.
Water-soluble contrast is used if perforation is suspected.
Thick barium is used in detection of mucosal irregularities and strictures while thin barium is used in motility assessment and detecting leaks.
Step 2: Imaging Protocol
The study is performed under real-time fluoroscopy with spot radiographs taken at specific times.
In the upright swallow test the patient swallows a sip of thin barium while real-time fluoroscopy captures their passage.
In multiple swallows with different contrast consistencies, it evaluates motility, peristalsis, and potential strictures.
In supine or prone swallow, it checks the esophageal obstruction and reflux under gravity-free conditions.
In rapid swallowing sequence, the patient should take consecutive swallows to test esophageal emptying and motility disorders.
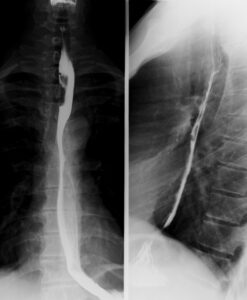
Esophagus with barium swallow
Complications
Barium Peritonitis or Mediastinitis
Aspiration of Barium
Contrast Allergy
Constipation/Impaction
Cumulative radiation exposure
Discomfort/Nausea
Vasovagal Reaction

Esophagography is a radiographic (X-ray) examination study of the esophagus. It includes ingesting barium or water-soluble contrast to visualize esophageal structure and function.
Barium sulfate was introduced in the 1900s to enhance gastrointestinal tract imaging
Fluoroscopy enhanced esophagography for real-time swallowing assessment.
Non-invasive procedure using barium sulfate to outline the esophagus.
Barium esophagography assesses swallowing, motility, reflux, and structural abnormalities of the esophagus and pharynx.
The pharyngeal phase involves dynamic recordings and double-contrast images to assess oral and pharyngeal function.
The risk of aspiration pneumonia increased with swallowing dysfunction while patients with silent aspiration faced nearly 15 times greater risk than those with normal swallowing.
Patient gulps low-density barium to distend esophagus and identify potential rings or strictures
Indications:
Structural abnormalities
Motility disorders
Foreign body obstruction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Post-surgical evaluation
Dysphagia
Odynophagia
Esophageal Obstruction
Contraindications:
Known or Suspected Barium Allergy
Acute Esophageal Perforation
Severe Dysphagia or Aspiration Risk
Suspected Tracheoesophageal
Severe Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Severe Debilitation
Outcomes:
The test offers essential diagnostic insights for esophageal management and function.
Cervical webs show as thin folds in anterior cervical esophagus barium studies.
Webs may extend circumferentially with deeper anterior shelf. Many patients show no symptoms, but dysphagia occurs with over 50% lumen obstruction.
Ruptured cervical esophageal webs are unrecognizable during endoscopy.
Frontal and lateral double-contrast views in pharyngeal cancer patients show contour disruption due to a mass protruding into the lumen.
Fluoroscopy Unit
X-ray Generator & Digital Recorder
Lead Shields & Radiation Protection Gear
Ancillary Equipment & Supplies
Patients must fast 4 to 8 hours before the procedure for clear esophagus views.
Patients on diabetes medications may need dose adjustments while fasting.
Check for barium or iodine allergy before using contrast agents.
Minimize radiation exposure for pregnant patients. Evaluate aspiration risk for stroke and neuromuscular patients.
Informed Consent:
Explain the procedure’s risks and potential complications clearly to the patient.
Patient should be positioned in upright and supine position for a complete assessment.
Patient examined upright and supine to assess entire esophagus.
Step 1: Administration of Contrast
Barium sulfate is preferred for most cases.
Water-soluble contrast is used if perforation is suspected.
Thick barium is used in detection of mucosal irregularities and strictures while thin barium is used in motility assessment and detecting leaks.
Step 2: Imaging Protocol
The study is performed under real-time fluoroscopy with spot radiographs taken at specific times.
In the upright swallow test the patient swallows a sip of thin barium while real-time fluoroscopy captures their passage.
In multiple swallows with different contrast consistencies, it evaluates motility, peristalsis, and potential strictures.
In supine or prone swallow, it checks the esophageal obstruction and reflux under gravity-free conditions.
In rapid swallowing sequence, the patient should take consecutive swallows to test esophageal emptying and motility disorders.

Esophagus with barium swallow
Barium Peritonitis or Mediastinitis
Aspiration of Barium
Contrast Allergy
Constipation/Impaction
Cumulative radiation exposure
Discomfort/Nausea
Vasovagal Reaction

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



