Background
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy is a surgical procedure which is used to remove the left adrenal gland as it is a minimally invasive procedure. Many laparoscopic procedures like lateral or posterior retroperitoneal and transthoracic are possible because of the location of the adrenal gland. Laparoscopy development brings a revolution in surgery, where surgeon can treat the adrenal disease with less morbidity.
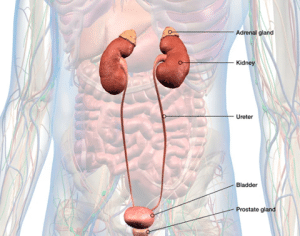
Anatomical identification of adrenal gland
Indications
The main indication of LA is a single malignant adrenal lesion. Incidentalomas, pheochromocytomas, aldosterone, Cushing’s syndrome, adrenal cysts, myelolipomas, androgen-secreting tumors, ganglioneuromas, and adrenal bleeding are the common indications to perform LA procedure. Bilateral LA is performed in Cushing’s syndrome in patients who are resistant to medical treatment and bilateral adrenal neoplasm. Surgeons must avoid treating the lesions which is >8 cm.
It is important to diagnose adrenal lesions accurately. Adrenal lesions can release cortisol, aldosterone, or catecholamines. When there is an adrenal lesion, hormones become active, and then extirpation procedure is suggested.
There is a high risk of bigger lesions. Radiographic and pathologic data are analyzed. About 95% of the adrenocortical carcinomas are bigger than 5 cm in diameter.
Contraindications
Tumors which are larger than 12 cm like malignancy or local tumor invasion into the tissue are contraindicated. The effectiveness of LA to treat adrenocortical cancer and metastatic adrenal disease is still not clear. Substantial cardiac disease, morbid density, coagulopathy and other diseases are not treated with LA and are contraindicated.
When adrenocortical cancer is seen, open adrenalectomy is suggested.
Many studies have explained the surgical procedures which are used to remove adrenal lesions. The 2 most common laparoscopic methods are transperitoneal and retroperitoneal. Transgastric samples extraction is a mini laparoscopic method.
Outcomes
Patient preparation
The patient is lying in the lateral decubitus at 60° and 90°. All pressure points are properly padded. The bed is tilted and an axillary role is placed. Kidney rest is extended to iliac crest. The arms are fixed in the anatomic position.
A beanbag is used to help to keep the patient on the table. The arms are protected by padding. The contralateral arm is placed on arm board and propped with cushions and attached with tape.
Left adrenalectomy
Step 1: Preparation:
An incision is made along with a white line of Toldt. It extends from splenic flexure to sigmoid junction. It enhances the mobilization of the left colon. The descending colon is seen and structures like phrenicocolic and splenorenal ligament allow the colon to slip away from the view. Dissection is performed between the Gerota fascia and the mesocolon. It goes to the renal and adrenal veins. The lateral 4th trocar is used to attach the PEER retractor to self-contained Endoholder.
Step 2: Port Placement
Before the adrenal vein is removed and cut the vasculature is identified. If it is not detected, the gonadal vein must be detected. It is present below renal hilum and renal vein. The adrenal vein enters renal vein from the termination of gonadal vein.
Step 3: Dissection of the Adrenal Gland
The lateral 4th trocar connects to the PEER retractor to self-contained Endoholder. It is used to remove the kidney during the dissection of adrenal gland. The vasculature is detected before the adrenal vein is removed and cut. If it is not detected then gonadal vein should be detected. It is present below the renal hilum and renal vein. Insert the adrenal vein into the renal vein through the termination of gonadal vein.
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy
Step 4: Removal of the Adrenal Gland
The medical dissection is performed from the renal vein in a cephalad position. Lateral dissection is performed between the perinephric fat and renal complex which is present next to the adrenal gland. This area is avascular, upper pole renal vessels must be avoided. Release the adrenal gland and periadrenal fat from the abdomen. The left inferior phrenic vein is present during the superior dissection. It should be detected and separated to reduce the excessive bleeding risk.
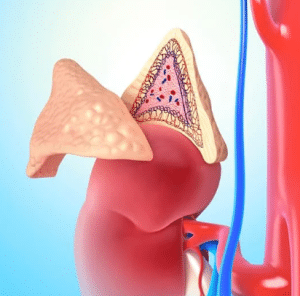
Removal of adrenal gland
Step 5: Closure
The dissected gland is placed on an endo pouch. It brought to the camera port. This stage include a 5 mm laparoscope. A 10 mm incision is made to remove the sample. It is closed by a polydioxanone suture.
Right adrenalectomy
Step 1: Preparation
The 1st or starting step is to divide the triangle ligament. Withdraw the liver with a locking grasper through the epigastric trocar. The grasper retracts the liver while holding a peritoneal or diaphragmatic fold on the lateral abdominal wall. The colon seldom needs much mobilization. The IVC must be located lateral and posterior to gallbladder at this stage.
Step 2: Dissection of the Adrenal Gland
Dissection is made to peritoneum incision and extends to the vena cava lateral border to the superior margin of the renal vein. The dissection is made posterior and exposes the superior portion of renal vein. The posterior abdominal wall encounters by protecting the renal artery and branches. The inferior adrenal gland and periadrenal tissue should withdraw with PEER retractor.
Step 3: Removal of the Adrenal Gland
Small branches of inferior phrenic artery may be seen and cauterized with bipolar tools. Dissection of gland is performed carefully on the side of IVC wall is approximated to adrenal gland. The adrenal may extend to the cava and dissection is completed by the IVC wall while gently retracting IVC. Lateral dissection is carried out the same way as left adrenalectomy.
Step 4: Closure
The sample is extracted by Endo Pouch. The incision is closed with zero polydioxanone suture. If the tumor is significant, a separate lower midline or Pfannenstiel incision may be needed to remove samples.
Complication:
Minor liver injury may occur after retraction or adrenal dissection on to the right side. Hemostatic is achieved by bipolar coagulation and endo peanut compression. The argon beam can be useful to control bleeding. Coagulation medications can be used to treat minor caval injury. By increasing the intra-abdominal pressure to 20 mm Hg, this will help to reduce the bleeding. If bleeding is not stopped then laparoscopic suturing and trocar implantation can be needed.

Laparoscopic adrenalectomy is a surgical procedure which is used to remove the left adrenal gland as it is a minimally invasive procedure. Many laparoscopic procedures like lateral or posterior retroperitoneal and transthoracic are possible because of the location of the adrenal gland. Laparoscopy development brings a revolution in surgery, where surgeon can treat the adrenal disease with less morbidity.

Anatomical identification of adrenal gland
The main indication of LA is a single malignant adrenal lesion. Incidentalomas, pheochromocytomas, aldosterone, Cushing’s syndrome, adrenal cysts, myelolipomas, androgen-secreting tumors, ganglioneuromas, and adrenal bleeding are the common indications to perform LA procedure. Bilateral LA is performed in Cushing’s syndrome in patients who are resistant to medical treatment and bilateral adrenal neoplasm. Surgeons must avoid treating the lesions which is >8 cm.
It is important to diagnose adrenal lesions accurately. Adrenal lesions can release cortisol, aldosterone, or catecholamines. When there is an adrenal lesion, hormones become active, and then extirpation procedure is suggested.
There is a high risk of bigger lesions. Radiographic and pathologic data are analyzed. About 95% of the adrenocortical carcinomas are bigger than 5 cm in diameter.
Tumors which are larger than 12 cm like malignancy or local tumor invasion into the tissue are contraindicated. The effectiveness of LA to treat adrenocortical cancer and metastatic adrenal disease is still not clear. Substantial cardiac disease, morbid density, coagulopathy and other diseases are not treated with LA and are contraindicated.
When adrenocortical cancer is seen, open adrenalectomy is suggested.
Many studies have explained the surgical procedures which are used to remove adrenal lesions. The 2 most common laparoscopic methods are transperitoneal and retroperitoneal. Transgastric samples extraction is a mini laparoscopic method.
The patient is lying in the lateral decubitus at 60° and 90°. All pressure points are properly padded. The bed is tilted and an axillary role is placed. Kidney rest is extended to iliac crest. The arms are fixed in the anatomic position.
A beanbag is used to help to keep the patient on the table. The arms are protected by padding. The contralateral arm is placed on arm board and propped with cushions and attached with tape.
Step 1: Preparation:
An incision is made along with a white line of Toldt. It extends from splenic flexure to sigmoid junction. It enhances the mobilization of the left colon. The descending colon is seen and structures like phrenicocolic and splenorenal ligament allow the colon to slip away from the view. Dissection is performed between the Gerota fascia and the mesocolon. It goes to the renal and adrenal veins. The lateral 4th trocar is used to attach the PEER retractor to self-contained Endoholder.
Step 2: Port Placement
Before the adrenal vein is removed and cut the vasculature is identified. If it is not detected, the gonadal vein must be detected. It is present below renal hilum and renal vein. The adrenal vein enters renal vein from the termination of gonadal vein.
Step 3: Dissection of the Adrenal Gland
The lateral 4th trocar connects to the PEER retractor to self-contained Endoholder. It is used to remove the kidney during the dissection of adrenal gland. The vasculature is detected before the adrenal vein is removed and cut. If it is not detected then gonadal vein should be detected. It is present below the renal hilum and renal vein. Insert the adrenal vein into the renal vein through the termination of gonadal vein.

Laparoscopic adrenalectomy
Step 4: Removal of the Adrenal Gland
The medical dissection is performed from the renal vein in a cephalad position. Lateral dissection is performed between the perinephric fat and renal complex which is present next to the adrenal gland. This area is avascular, upper pole renal vessels must be avoided. Release the adrenal gland and periadrenal fat from the abdomen. The left inferior phrenic vein is present during the superior dissection. It should be detected and separated to reduce the excessive bleeding risk.

Removal of adrenal gland
Step 5: Closure
The dissected gland is placed on an endo pouch. It brought to the camera port. This stage include a 5 mm laparoscope. A 10 mm incision is made to remove the sample. It is closed by a polydioxanone suture.
Step 1: Preparation
The 1st or starting step is to divide the triangle ligament. Withdraw the liver with a locking grasper through the epigastric trocar. The grasper retracts the liver while holding a peritoneal or diaphragmatic fold on the lateral abdominal wall. The colon seldom needs much mobilization. The IVC must be located lateral and posterior to gallbladder at this stage.
Step 2: Dissection of the Adrenal Gland
Dissection is made to peritoneum incision and extends to the vena cava lateral border to the superior margin of the renal vein. The dissection is made posterior and exposes the superior portion of renal vein. The posterior abdominal wall encounters by protecting the renal artery and branches. The inferior adrenal gland and periadrenal tissue should withdraw with PEER retractor.
Step 3: Removal of the Adrenal Gland
Small branches of inferior phrenic artery may be seen and cauterized with bipolar tools. Dissection of gland is performed carefully on the side of IVC wall is approximated to adrenal gland. The adrenal may extend to the cava and dissection is completed by the IVC wall while gently retracting IVC. Lateral dissection is carried out the same way as left adrenalectomy.
Step 4: Closure
The sample is extracted by Endo Pouch. The incision is closed with zero polydioxanone suture. If the tumor is significant, a separate lower midline or Pfannenstiel incision may be needed to remove samples.
Complication:
Minor liver injury may occur after retraction or adrenal dissection on to the right side. Hemostatic is achieved by bipolar coagulation and endo peanut compression. The argon beam can be useful to control bleeding. Coagulation medications can be used to treat minor caval injury. By increasing the intra-abdominal pressure to 20 mm Hg, this will help to reduce the bleeding. If bleeding is not stopped then laparoscopic suturing and trocar implantation can be needed.

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



