Background
Myelography is a procedure in which the spinal cord, nerve roots, and other structures are seen using a contrast agent. It consists of administering a contrast dye into the subarachnoid space, which often involves a lumbar puncture. This dye increases the contrast of the spine and nerve structures on the X-ray, CT scan, or MRI.
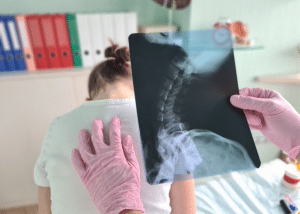
Indications
Contraindications
Outcomes
Equipment
Patient Preparation
Patient History and Consent:
Take a comprehensive case history on the patient medical history in terms of their disease, allergies to any compounds such as contrast media or iodine, current and past medicines as well as past procedures done.
Discuss the procedure, risks, benefits and any side effects that might be associated with genomic sequencing should be explained to the patient.
Obtain written informed consent.
Medication Review:
Evaluate the current medications the patient is currently using. Anticoagulants and some other medicines may be taken a few days prior to the procedure.
Because one is diabetic, the patient should consult their physician about how the fasting will impact the insulin level.
Fasting:
The patient can only take food or drink after the procedure in 4 to 8 hours.
Hydration:
Remind the patient to intake sufficient fluids before arriving when they cannot consume food or fluids before the surgery.
Clothing and Personal Items:
Loose and comfortable clothing should be worn by the patient.
All jewellery, watches, and other metal items should be taken off for these can affect the images taken.
Premedication:
Give any preoperative medications, usually a mild sedative, before the procedure to help calm the patient.
Technique
Step 1-Positioning the Patient:
Place the patient on the X-ray table laying on their side or entirely on their abdomen.
Step 2-Sterilization and Local Anesthesia:
Wipe the lumbar area of the patient with an appropriate antiseptic agent.
Cover the environment around the patient with sterile towels.
Give an injection of lidocaine to help local anesthetic for the puncture.
Step 3-Lumbar Puncture:
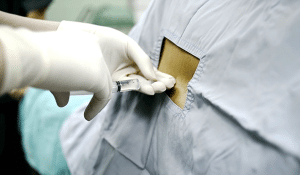
Puncture the subarachnoid space using a spinal needle, commonly between intervertebral space.
Assure the correct position of the needle by checking the drip of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Step 4-Contrast Medium Injection:
Connect a syringe with the contrast medium to the spinal needle.
Administer the contrast medium into the subarachnoid space gradually.
Take out the spinal needle once the injection has been made.
Step 5-Imaging:
Position the patient as required for imaging. Usually, it is used to take several views of the spine where many positions are involved.
Assess the flow of the contrast medium through X-ray images or CT scans.
The possible side effects of the contrast medium should also be observed in the patient.
Step 6-Post-procedure
Observation:
Keep the patient in a supine position for a few hours to prevent headaches caused by CSF leakage.
Observe for the manifestations of allergy or any complication that may occur in the patient.
Post-procedure Care:
For elimination of the contrast medium from the body, the patient should be encouraged to take plenty of fluids.
Avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 hours.
Laboratory tests
Blood Tests:
Allergy Tests:
Complications

Myelography is a procedure in which the spinal cord, nerve roots, and other structures are seen using a contrast agent. It consists of administering a contrast dye into the subarachnoid space, which often involves a lumbar puncture. This dye increases the contrast of the spine and nerve structures on the X-ray, CT scan, or MRI.

Patient History and Consent:
Take a comprehensive case history on the patient medical history in terms of their disease, allergies to any compounds such as contrast media or iodine, current and past medicines as well as past procedures done.
Discuss the procedure, risks, benefits and any side effects that might be associated with genomic sequencing should be explained to the patient.
Obtain written informed consent.
Medication Review:
Evaluate the current medications the patient is currently using. Anticoagulants and some other medicines may be taken a few days prior to the procedure.
Because one is diabetic, the patient should consult their physician about how the fasting will impact the insulin level.
Fasting:
The patient can only take food or drink after the procedure in 4 to 8 hours.
Hydration:
Remind the patient to intake sufficient fluids before arriving when they cannot consume food or fluids before the surgery.
Clothing and Personal Items:
Loose and comfortable clothing should be worn by the patient.
All jewellery, watches, and other metal items should be taken off for these can affect the images taken.
Premedication:
Give any preoperative medications, usually a mild sedative, before the procedure to help calm the patient.
Step 1-Positioning the Patient:
Place the patient on the X-ray table laying on their side or entirely on their abdomen.
Step 2-Sterilization and Local Anesthesia:
Wipe the lumbar area of the patient with an appropriate antiseptic agent.
Cover the environment around the patient with sterile towels.
Give an injection of lidocaine to help local anesthetic for the puncture.
Step 3-Lumbar Puncture:

Puncture the subarachnoid space using a spinal needle, commonly between intervertebral space.
Assure the correct position of the needle by checking the drip of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Step 4-Contrast Medium Injection:
Connect a syringe with the contrast medium to the spinal needle.
Administer the contrast medium into the subarachnoid space gradually.
Take out the spinal needle once the injection has been made.
Step 5-Imaging:
Position the patient as required for imaging. Usually, it is used to take several views of the spine where many positions are involved.
Assess the flow of the contrast medium through X-ray images or CT scans.
The possible side effects of the contrast medium should also be observed in the patient.
Step 6-Post-procedure
Observation:
Keep the patient in a supine position for a few hours to prevent headaches caused by CSF leakage.
Observe for the manifestations of allergy or any complication that may occur in the patient.
Post-procedure Care:
For elimination of the contrast medium from the body, the patient should be encouraged to take plenty of fluids.
Avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 hours.
Blood Tests:
Allergy Tests:

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



