Background
Scintigraphy uses gamma rays from radioactive isotopes to create images of internal organs and tissues.
Nuclear medicine imaging detects gamma radiation from a radioactive tracer injected into the body.
Nuclear medicine principles originated from Becquerel’s radioactivity discovery. Radioisotope uses in medicine started with iodine for thyroid.
Advancements in radiopharmaceuticals and imaging, particularly SPECT and PET, have improved diagnostic accuracy through precise and functional imaging techniques.
Radioactive tracer is injected into the body in small amounts. Captured images assist in diagnosing cancer and infections.
The tracer emits gamma rays in the target organ, which a gamma camera detects and images.
Procedure imaging internal body structures and cancer cell locations.
Scintigraphy uses radioisotopes in drugs to diagnose organ conditions.
Indications
Detection of Tumors and Metastases
Evaluation of Treatment Response
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Cardiac Function Studies
Brain Scintigraphy/PET
Ventilation-Perfusion Scan
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Scintigraphy
Gastric Emptying Study
Hepatobiliary System
Nephrology/Urology
Orthopedics & Infection Imaging
Contraindications
Severe Allergy to Radiopharmaceuticals
Pregnancy
Breastfeeding Mothers
Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Recent Use of Iodine-Based Contrast Media
Uncooperative Patients
Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
Outcomes
Radiotracer uptake is within expected physiological limits.
Symmetrical distribution without abnormal hot or cold areas. Normal organ function, perfusion, and clearance.
It decreased tracer uptake during stress but normal at rest. Persistent defect in uptake indicates prior myocardial damage.
It reduced uptake in the temporal and parietal lobes. Decreased dopamine transporter activity in the basal ganglia.
Equipment required
Radiopharmaceuticals & Delivery System
Dose Calibrator
Radiation Shielding & Safety Equipment
Gamma Camera
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Scanner
Positron Emission Tomography Scanner
Image Analysis Equipment
Patient Preparation:
Assess for allergies, pregnancy, kidney dysfunction, or recent contrast use.
Gastric emptying scan requires fasting for 4 to 6 hours.
For myocardial perfusion scan: Avoid caffeine and nicotine intake for 12 to 24 hours.
For thyroid scan: Avoid iodine-containing foods for 4 to 6 weeks.
Informed Consent:
Explain the procedure’s risks and potential complications clearly to the patient.
Patient Positioning:
Patients should remain still while imaging to avoid motion artifacts.
Technique
Step 1: Radiopharmaceutical administration
A small number of radioactive tracers are introduced in the body.
The radiopharmaceutical accumulates in the target organ based on its physiological properties.
Step 2: Uptake and Biodistribution Phase
After administration, the tracer requires a certain time to localize in the target organ. The waiting period is as follows:
For Bone Scan: 2 to 4 hours
For Thyroid Scan: 24 hours
Step 3: Gamma Camera Imaging
A gamma camera detects the gamma radiation emitted from the tracer.
The camera can be positioned over the target organ to capture images in static, dynamic, or tomographic modes.
Step 4: Image Processing and Reconstruction
The detected gamma rays are converted into digital images using software.
Color images show areas of increased or decreased uptake.
Advanced processing includes fusion imaging for anatomical correlation.
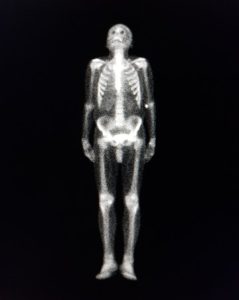
Scintigraphy of bone
Complications:
Allergic Reactions
Radiation Exposure Risks
Iodine-Based Radiopharmaceutical Issues
Kidney-Related Concerns
Injection-Site Reactions
Vasovagal Reaction
Claustrophobia or Anxiety
Radiation Contamination Risk
Temporary Breastfeeding Interruption

Scintigraphy uses gamma rays from radioactive isotopes to create images of internal organs and tissues.
Nuclear medicine imaging detects gamma radiation from a radioactive tracer injected into the body.
Nuclear medicine principles originated from Becquerel’s radioactivity discovery. Radioisotope uses in medicine started with iodine for thyroid.
Advancements in radiopharmaceuticals and imaging, particularly SPECT and PET, have improved diagnostic accuracy through precise and functional imaging techniques.
Radioactive tracer is injected into the body in small amounts. Captured images assist in diagnosing cancer and infections.
The tracer emits gamma rays in the target organ, which a gamma camera detects and images.
Procedure imaging internal body structures and cancer cell locations.
Scintigraphy uses radioisotopes in drugs to diagnose organ conditions.
Detection of Tumors and Metastases
Evaluation of Treatment Response
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Cardiac Function Studies
Brain Scintigraphy/PET
Ventilation-Perfusion Scan
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Scintigraphy
Gastric Emptying Study
Hepatobiliary System
Nephrology/Urology
Orthopedics & Infection Imaging
Severe Allergy to Radiopharmaceuticals
Pregnancy
Breastfeeding Mothers
Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Recent Use of Iodine-Based Contrast Media
Uncooperative Patients
Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
Radiotracer uptake is within expected physiological limits.
Symmetrical distribution without abnormal hot or cold areas. Normal organ function, perfusion, and clearance.
It decreased tracer uptake during stress but normal at rest. Persistent defect in uptake indicates prior myocardial damage.
It reduced uptake in the temporal and parietal lobes. Decreased dopamine transporter activity in the basal ganglia.
Radiopharmaceuticals & Delivery System
Dose Calibrator
Radiation Shielding & Safety Equipment
Gamma Camera
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Scanner
Positron Emission Tomography Scanner
Image Analysis Equipment
Patient Preparation:
Assess for allergies, pregnancy, kidney dysfunction, or recent contrast use.
Gastric emptying scan requires fasting for 4 to 6 hours.
For myocardial perfusion scan: Avoid caffeine and nicotine intake for 12 to 24 hours.
For thyroid scan: Avoid iodine-containing foods for 4 to 6 weeks.
Informed Consent:
Explain the procedure’s risks and potential complications clearly to the patient.
Patient Positioning:
Patients should remain still while imaging to avoid motion artifacts.
Step 1: Radiopharmaceutical administration
A small number of radioactive tracers are introduced in the body.
The radiopharmaceutical accumulates in the target organ based on its physiological properties.
Step 2: Uptake and Biodistribution Phase
After administration, the tracer requires a certain time to localize in the target organ. The waiting period is as follows:
For Bone Scan: 2 to 4 hours
For Thyroid Scan: 24 hours
Step 3: Gamma Camera Imaging
A gamma camera detects the gamma radiation emitted from the tracer.
The camera can be positioned over the target organ to capture images in static, dynamic, or tomographic modes.
Step 4: Image Processing and Reconstruction
The detected gamma rays are converted into digital images using software.
Color images show areas of increased or decreased uptake.
Advanced processing includes fusion imaging for anatomical correlation.

Scintigraphy of bone
Complications:
Allergic Reactions
Radiation Exposure Risks
Iodine-Based Radiopharmaceutical Issues
Kidney-Related Concerns
Injection-Site Reactions
Vasovagal Reaction
Claustrophobia or Anxiety
Radiation Contamination Risk
Temporary Breastfeeding Interruption

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.

On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.

When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.



