Sleepless and Costly: How OSA Is Hitting US and UK Workforces
March 3, 2026
Background
Amebiasis or amoebic dysentery is a parasite enteral disease. It is caused by Entamoeba genus amoeba. It causes mild to severe symptoms like bloody diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or no symptoms. This parasite may enter into the bloodstream and go to liver. This can lead to an amoebic hepatic abscess. Stool samples and blood tests are required to diagnose the disease. Amoebiasis can be found globally. It affects about 40,000 to 100,000 people per year.
Epidemiology
Amebiasis mostly occurs in underdeveloped countries because of poor sanitation and elevating fecal contamination to drinking water sources. Amebiasis is an ailment. It affects over 50 million people globally. Infected food or water consumption by feces which contains E. histolytica larvae can cause infection. E. histolytica can survive in environment for longer periods in its cyclic condition. It is also got by penetrative and anal sex, direct rectum inoculation or colon irrigation equipment. There are no vaccinations or preventative drugs for amebiasis.
Anatomy
Pathophysiology
Protozoa infection of E. histolytica generates pseudopods and lyses tissue and causes proteolysis. Consuming mature cysts by feces contaminated hands, water, or food can lead to this condition. The small bowel goes excystation of the developed cysts and releases trophozoites. This can go to large bowel. Binary fission produces cysts as the trophozoites grow. Both stages exit via feces. The cysts can survive for days to 7 weeks in the environment.
Etiology
Amebiasis is caused by parasite Entamoeba histolytica. There are 3 different species of intestinal amoeba. Many symptomatic diseases occur by Entamoeba histolytica. Entamoeba dispar is not pathogenic. Entamoeba moshkovskii is more prevalent. It is now known it is pathogenic or not. The oral-fecal pathway is the way to proliferate. Contaminated food and water can cause infectious cysts. Rare cases of sexual transmission have been found.
Genetics
Prognostic Factors
Amoebic infections have a very high risk of morbidity and mortality. Malaria can lead to death.
The below demographics have the most severe amoebic infestations:
Postpartum females
People who are underweight
Neonates
Pregnant women
People who take corticosteroids
People who have malignancies
The prognosis is good if the disease is treated. Infestations recurrence is common in many regions of the world. < 1% of patients die after the treatment. An intraperitoneal puncture may remove an amoebic abscess in 5 to 10% of cases. It increases the fatality rate. The fatality rate of amoebic pericarditis & bronchial amebiasis is about 20%. Fatality rate in patients who have uncomplicated diseases are below 1 % wit intense treatment. An infected amoebic hepatic disease is a significant disease which increases the mortality rate.
Clinical History
Asymptomatic Infection: Many people who are infected with E. histolytica may have no symptoms, specifically in regions with endemic amoebiasis.
Intestinal Amebiasis:
Age Group:
This disease can affect all individuals from all ages. Severe complications commonly occurred in older adults and young children.
Physical Examination
Age group
Associated comorbidity
Associated activity
Acuity of presentation
The acuity of presentation may vary from mild to severe cases of disease. Seve cases may have acute abdominal pain, signs of systemic inflammation and high fever.
Differential Diagnoses
Laboratory Studies
Imaging Studies
Procedures
Histologic Findings
Staging
Treatment Paradigm
Asymptomatic or Mild Intestinal Amebiasis:
Moderate to Severe Intestinal Amebiasis:
Extraintestinal Amebiasis (Liver Abscess):
by Stage
by Modality
Chemotherapy
Radiation Therapy
Surgical Interventions
Hormone Therapy
Immunotherapy
Hyperthermia
Photodynamic Therapy
Stem Cell Transplant
Targeted Therapy
Palliative Care
use-of-a-non-pharmacological-approach-for-treating-amebiasis
Use of metronidazole in the treatment of amebiasis
Metronidazole is an important antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It inhibits synthesis of nucleic acid and causes cell death by interfering the structure of DNA. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. It is available in forms of oral formulations and taken after the meal to improve absorption and reduce the stomach discomforts.
Use of Tinidazole in the treatment of Amebiasis
Tinidazole is an antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis. It disrupts the structure of DNA and function of microbial cells, inhibits the synthesise if nucleic acid and lead to cell death. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. The dose of medication is dependent on the severity and symptoms of disease. The usual dosage id 2 gm per day for 2 to 3 days.
Use of Luminal agents like paromomycin and diloxanide furoate in the treatment of Amebiasis
Luminal agents like paromomycin and diloxanide furoate are used to treat amebiasis in luminal phase of Entamoeba histolytica. This medication is prescribed along with tissue amebicides like tinidazole or metronidazole.
use-of-intervention-with-a-procedure-in-treating-amebiasis
Surgical Intervention:
use-of-phases-to-manage-amebiasis
Medication
Indicated for Amebiasis, Intestinal:
2g/day orally for three days
500 mg of the drug to be taken orally every 12 hours for 5 to 10 days
35-50 mg/kg orally every 8 hours for 10 days
Indicated for extraintestinal amebiasis
1000 mg salt (with 600 mg base) orally each day for 2 days
500 mg salt (with 300 mg base) each day for 14-21 days
Future Trends
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519535/
Amebiasis or amoebic dysentery is a parasite enteral disease. It is caused by Entamoeba genus amoeba. It causes mild to severe symptoms like bloody diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or no symptoms. This parasite may enter into the bloodstream and go to liver. This can lead to an amoebic hepatic abscess. Stool samples and blood tests are required to diagnose the disease. Amoebiasis can be found globally. It affects about 40,000 to 100,000 people per year.
Amebiasis mostly occurs in underdeveloped countries because of poor sanitation and elevating fecal contamination to drinking water sources. Amebiasis is an ailment. It affects over 50 million people globally. Infected food or water consumption by feces which contains E. histolytica larvae can cause infection. E. histolytica can survive in environment for longer periods in its cyclic condition. It is also got by penetrative and anal sex, direct rectum inoculation or colon irrigation equipment. There are no vaccinations or preventative drugs for amebiasis.
Protozoa infection of E. histolytica generates pseudopods and lyses tissue and causes proteolysis. Consuming mature cysts by feces contaminated hands, water, or food can lead to this condition. The small bowel goes excystation of the developed cysts and releases trophozoites. This can go to large bowel. Binary fission produces cysts as the trophozoites grow. Both stages exit via feces. The cysts can survive for days to 7 weeks in the environment.
Amebiasis is caused by parasite Entamoeba histolytica. There are 3 different species of intestinal amoeba. Many symptomatic diseases occur by Entamoeba histolytica. Entamoeba dispar is not pathogenic. Entamoeba moshkovskii is more prevalent. It is now known it is pathogenic or not. The oral-fecal pathway is the way to proliferate. Contaminated food and water can cause infectious cysts. Rare cases of sexual transmission have been found.
Amoebic infections have a very high risk of morbidity and mortality. Malaria can lead to death.
The below demographics have the most severe amoebic infestations:
Postpartum females
People who are underweight
Neonates
Pregnant women
People who take corticosteroids
People who have malignancies
The prognosis is good if the disease is treated. Infestations recurrence is common in many regions of the world. < 1% of patients die after the treatment. An intraperitoneal puncture may remove an amoebic abscess in 5 to 10% of cases. It increases the fatality rate. The fatality rate of amoebic pericarditis & bronchial amebiasis is about 20%. Fatality rate in patients who have uncomplicated diseases are below 1 % wit intense treatment. An infected amoebic hepatic disease is a significant disease which increases the mortality rate.
Asymptomatic Infection: Many people who are infected with E. histolytica may have no symptoms, specifically in regions with endemic amoebiasis.
Intestinal Amebiasis:
Age Group:
This disease can affect all individuals from all ages. Severe complications commonly occurred in older adults and young children.
The acuity of presentation may vary from mild to severe cases of disease. Seve cases may have acute abdominal pain, signs of systemic inflammation and high fever.
Asymptomatic or Mild Intestinal Amebiasis:
Moderate to Severe Intestinal Amebiasis:
Extraintestinal Amebiasis (Liver Abscess):
Emergency Medicine
Gastroenterology
Infectious Disease
Nutrition
Infectious Disease
Metronidazole is an important antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It inhibits synthesis of nucleic acid and causes cell death by interfering the structure of DNA. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. It is available in forms of oral formulations and taken after the meal to improve absorption and reduce the stomach discomforts.
Infectious Disease
Tinidazole is an antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis. It disrupts the structure of DNA and function of microbial cells, inhibits the synthesise if nucleic acid and lead to cell death. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. The dose of medication is dependent on the severity and symptoms of disease. The usual dosage id 2 gm per day for 2 to 3 days.
Infectious Disease
Luminal agents like paromomycin and diloxanide furoate are used to treat amebiasis in luminal phase of Entamoeba histolytica. This medication is prescribed along with tissue amebicides like tinidazole or metronidazole.
Surgical Intervention:
Critical Care/Intensive Care
Emergency Medicine
Nutrition
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519535/
Amebiasis or amoebic dysentery is a parasite enteral disease. It is caused by Entamoeba genus amoeba. It causes mild to severe symptoms like bloody diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or no symptoms. This parasite may enter into the bloodstream and go to liver. This can lead to an amoebic hepatic abscess. Stool samples and blood tests are required to diagnose the disease. Amoebiasis can be found globally. It affects about 40,000 to 100,000 people per year.
Amebiasis mostly occurs in underdeveloped countries because of poor sanitation and elevating fecal contamination to drinking water sources. Amebiasis is an ailment. It affects over 50 million people globally. Infected food or water consumption by feces which contains E. histolytica larvae can cause infection. E. histolytica can survive in environment for longer periods in its cyclic condition. It is also got by penetrative and anal sex, direct rectum inoculation or colon irrigation equipment. There are no vaccinations or preventative drugs for amebiasis.
Protozoa infection of E. histolytica generates pseudopods and lyses tissue and causes proteolysis. Consuming mature cysts by feces contaminated hands, water, or food can lead to this condition. The small bowel goes excystation of the developed cysts and releases trophozoites. This can go to large bowel. Binary fission produces cysts as the trophozoites grow. Both stages exit via feces. The cysts can survive for days to 7 weeks in the environment.
Amebiasis is caused by parasite Entamoeba histolytica. There are 3 different species of intestinal amoeba. Many symptomatic diseases occur by Entamoeba histolytica. Entamoeba dispar is not pathogenic. Entamoeba moshkovskii is more prevalent. It is now known it is pathogenic or not. The oral-fecal pathway is the way to proliferate. Contaminated food and water can cause infectious cysts. Rare cases of sexual transmission have been found.
Amoebic infections have a very high risk of morbidity and mortality. Malaria can lead to death.
The below demographics have the most severe amoebic infestations:
Postpartum females
People who are underweight
Neonates
Pregnant women
People who take corticosteroids
People who have malignancies
The prognosis is good if the disease is treated. Infestations recurrence is common in many regions of the world. < 1% of patients die after the treatment. An intraperitoneal puncture may remove an amoebic abscess in 5 to 10% of cases. It increases the fatality rate. The fatality rate of amoebic pericarditis & bronchial amebiasis is about 20%. Fatality rate in patients who have uncomplicated diseases are below 1 % wit intense treatment. An infected amoebic hepatic disease is a significant disease which increases the mortality rate.
Asymptomatic Infection: Many people who are infected with E. histolytica may have no symptoms, specifically in regions with endemic amoebiasis.
Intestinal Amebiasis:
Age Group:
This disease can affect all individuals from all ages. Severe complications commonly occurred in older adults and young children.
The acuity of presentation may vary from mild to severe cases of disease. Seve cases may have acute abdominal pain, signs of systemic inflammation and high fever.
Asymptomatic or Mild Intestinal Amebiasis:
Moderate to Severe Intestinal Amebiasis:
Extraintestinal Amebiasis (Liver Abscess):
Emergency Medicine
Gastroenterology
Infectious Disease
Nutrition
Infectious Disease
Metronidazole is an important antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It inhibits synthesis of nucleic acid and causes cell death by interfering the structure of DNA. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. It is available in forms of oral formulations and taken after the meal to improve absorption and reduce the stomach discomforts.
Infectious Disease
Tinidazole is an antimicrobial drug. It is used to treat amebiasis. It disrupts the structure of DNA and function of microbial cells, inhibits the synthesise if nucleic acid and lead to cell death. It is effective against both luminal and tissue forms of Entamoeba histolytica. The dose of medication is dependent on the severity and symptoms of disease. The usual dosage id 2 gm per day for 2 to 3 days.
Infectious Disease
Luminal agents like paromomycin and diloxanide furoate are used to treat amebiasis in luminal phase of Entamoeba histolytica. This medication is prescribed along with tissue amebicides like tinidazole or metronidazole.
Surgical Intervention:
Critical Care/Intensive Care
Emergency Medicine
Nutrition
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519535/

Both our subscription plans include Free CME/CPD AMA PRA Category 1 credits.
On course completion, you will receive a full-sized presentation quality digital certificate.
A dynamic medical simulation platform designed to train healthcare professionals and students to effectively run code situations through an immersive hands-on experience in a live, interactive 3D environment.
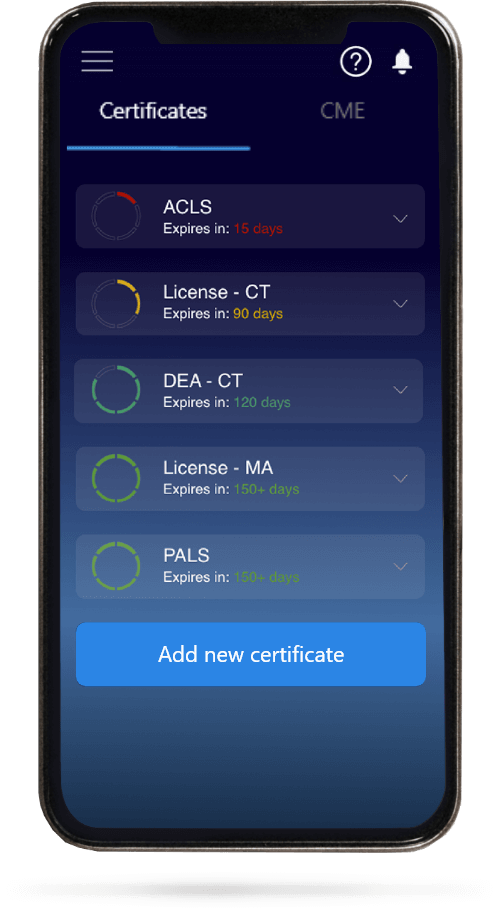
When you have your licenses, certificates and CMEs in one place, it's easier to track your career growth. You can easily share these with hospitals as well, using your medtigo app.